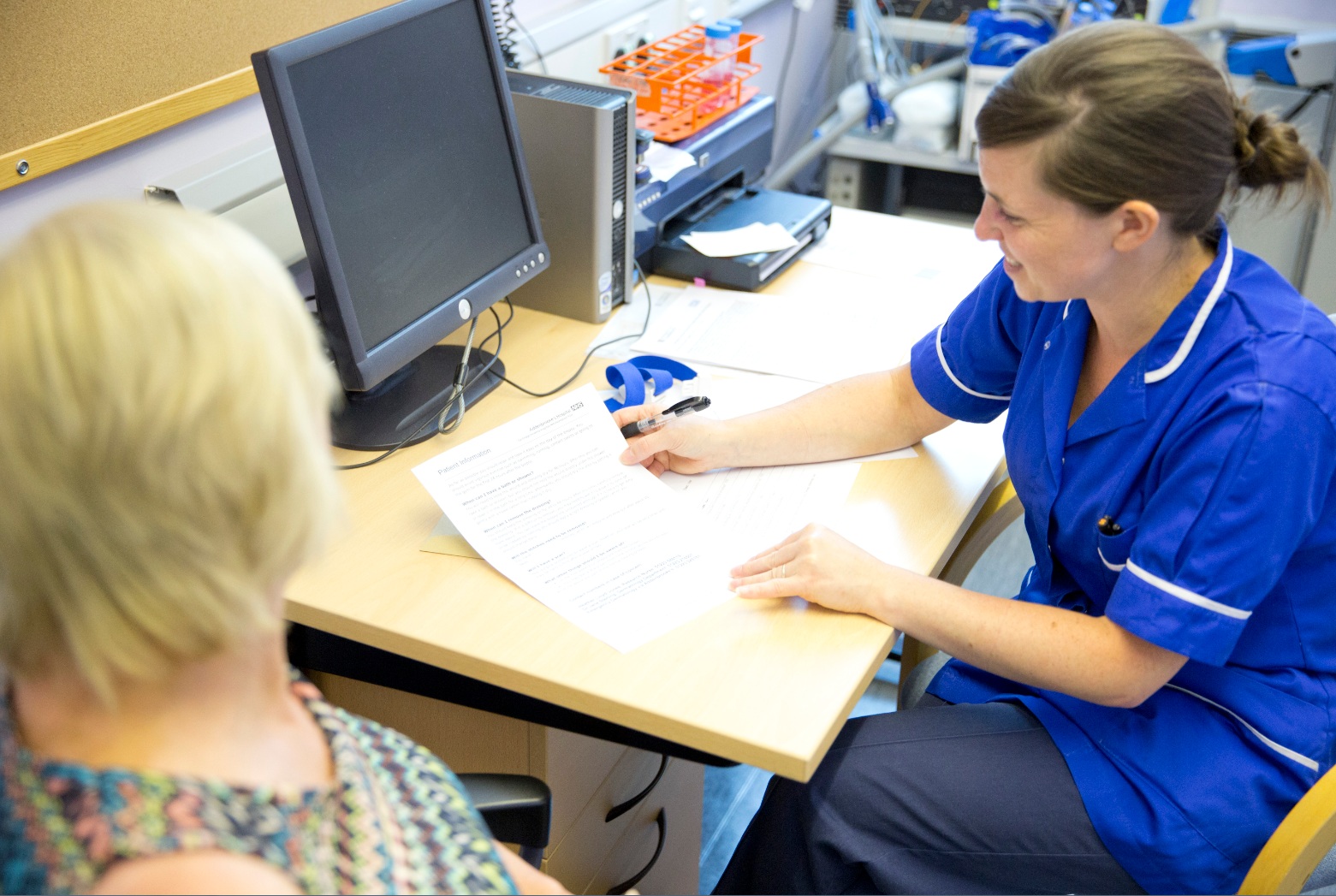
Taking part in research
Addenbrooke’s Hospital is a large research hospital linked to Cambridge University. We are dedicated to improving the health and well-being of people in our community through research, working in partnership with our patients.
We want as many people as possible to be able to make a difference through research, whether that is participating in research studies or getting involved in making sure our research meets the needs of our patients.
Telling us that you’re interested
If you’re interested in hearing about studies that might be relevant to you, you can register your interest on the Be Part of Research website. Researchers will then send you information about approved studies that match your interests and you can decide if you want to take part.
We also have worked on a project with MyChart called ‘Consent for Contact’, this enables you to give your permission for local research teams to contact you directly about studies you are eligible for. If you do not yet have a MyChart account, then as long as you are a patient at CUH you can register for an account. You will always be given information about any studies and you are free to choose whether or not to participate.
Studies for healthy volunteers
You don’t have to have a health condition to take part in research, people without a health condition can also make a very important contribution to research.
One of the ways you can take part in research by joining the NIHR BioResource. Watch the short video below to find out what being part of the NIHR BioResource involves.
You can also join health volunteer studies and contribute to research through the NIHR Cambridge Clinical Research Facility.
Studies for your health condition
You can find out about research studies that you might be eligible for by asking your doctor or health care team, or checking the national study registry at Be Part Of Research.
Getting involved
Patients, carers and members of the public have important lived experience and other expertise that can help researchers design and conduct better research for everyone.
You can find out more about why public involvement in research is important on our Patient and Public pages.
Useful Links:
- Join our Patient and Public Involvement panel: Panel members provide feedback on a wide variety of research projects taking place in Cambridge, mostly via email or virtual meetings.
- The NIHR Brain Injury MedTech Co-operative: has developed a volunteer register for patients, carers and other interested persons to assist in the development and advance of healthcare technologies.
- The NIHR BioResource: Join a panel of around 200,000 volunteers, both with and without health conditions, who are willing to be approached to participate in research studies investigating the links between genes, the environment, health and disease.
- The NIHR Cambridge Clinical Research Facility: A facility for patients and volunteers who are participating in research (both adults and children). It supports experimental medicine and early phase research studies.
- Cambridge Brain Bank: Established to enable brain tissue to be used after death for research into neurodegenerative disorders such as Dementia (Alzheimer’s, Frontotemportal etc.), Motor Neurone disease, Huntington’s disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease etc.
- Cambridge Cancer Trials Centre has trials running for many different kinds of cancer, alongside important information about how clinical trials work and why they are important.
- The Cambridge Patient Led Research Hub (PLRH) supports patient-led research, working in partnership with charities and patient groups to deliver clinical studies based on patients’ own research questions.
- Be Part of Research: Find out what it means to take part in a clinical trial, sign up for trials, look for trials relevant to you and contact researchers.
- NIHR People in Research: Opportunities for public involvement in NHS, public health and social care research.
Unfortunately we cannot provide specific health information or referrals to clinicians through these web pages. Further information about specific clinical trials can be found via:
- Contacting your doctor/ GP
- NIHR Be Part of Research
- NHS.uk